Respiratory Area
According to WHO data, there are about 210 million people with COPD, 65 million with moderate to severe COPD, causing 3 million deaths globally. (1),(3),(19) It is estimated that by 2030, COPD will be the third cause of death in the world. (1)
COPD
COPD is defined as a frequent, preventable and treatable disease characterized by persistent respiratory symptoms and limitation of airway flow resulting from alveolar and/or airway changes caused by significant exposure to harmful particles and gases. (2)
COPD has a high impact on both individuals and society
In addition to being a disabling disease associated with premature mortality, COPD is also associated with increased health care needs and hospital stays due to exacerbations. (1),(3),(4) The cost of COPD is more than just financial, as it affects the quality of life of patients and has a detrimental impact on their mental health (1),(2),(3)The prevalence of COPD is expected to increase in the coming decades. (2),(5)
Risk Factors (2)
- SMOKING
- Exposure to polluting gases, dust or chemicals
- Family History (rare and more frequent in individuals of European descent)
- Poor lung development (decreased lung function)
- Nutrition and Socioeconomic Status
- Respiratory infections (in childhood)
How does COPD cause airflow limitation?
The typical airflow limitation of COPD is caused by narrowing and/or obstruction of the airways, loss of elastic retraction, or both (6).
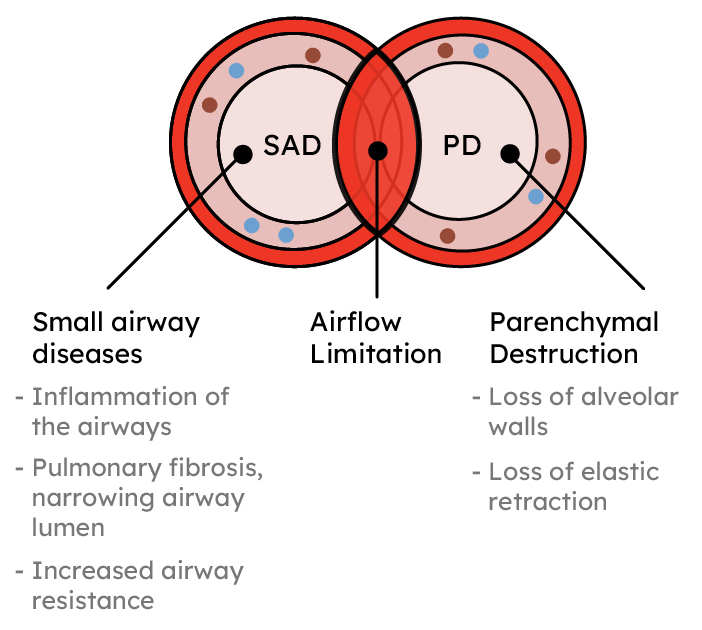
Adapted from 6
Symptoms
- Dyspnea is the distinctive symptom of COPD. It is usually persistent and progressive - also known as shortness of breath (7)
- Chronic cough (7)
- Wheezing (7)
What is an exacerbation? (8)
- It is an acute worsening of symptoms
- Increased shortness of breath during normal daily activities, with a consequent increase in the use of usual medication and/or need for medication.
- Sputum production, which can become more frequent than is normal for the patient, or be viscous;
- Cough that can occur due to increased sputum
Impact of exacerbations
- Increased airway inflammation
- Decreased quality of life (8)
- Increased mortality rate (8)
- Rapid decline in lung function (8)
Associated illnesses (9)
- Cardiovascular diseases (10),(11)
- Diabetes (12),(13)
- Depression(14)
- Osteoporosis(14),(15)
- Lung cancer (16)
- Weight loss (17)
Diagnosis (19)
The clinical diagnosis of COPD should be considered in any patient who has the following symptoms:
- Dyspnea, chronic cough or sputum
Airflow measurement by spirometry is required (2)
- presence of air flow obstruction due to spirometric changes (FEV1/FVC ratio below 0.70 after bronchodilation) (19)
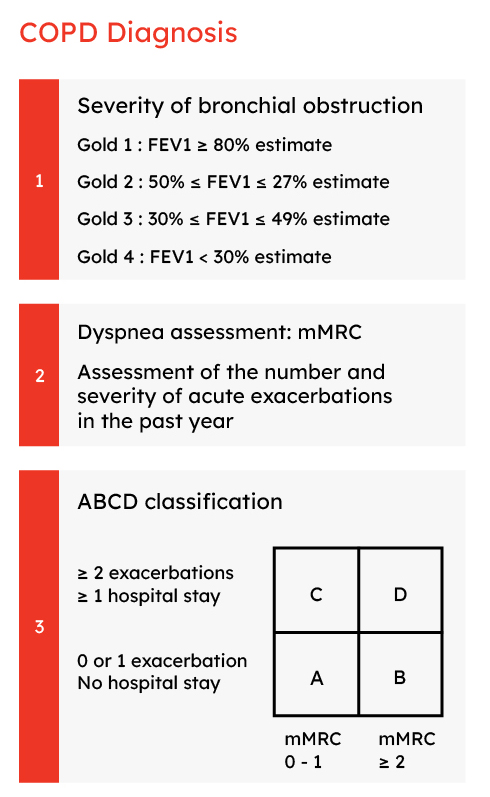
Adapted from 19
How are symptoms assessed?
- Medical Research Council (mMRC) modified dyspnea scale - assesses dyspnea intensity, ranging from zero to four.(2)
- COPD (CAT) assessment test questionnaire - Measures the impact of COPD on quality of life.(2)
- COPD clinical questionnaire (CCQ) - measures functional status, symptom and mental status), related to people with COPD.(2)
- Questionnaire about shortness of breath with daily activities (SOBDA) (18)
Treatment objectives
1. Reduction of current symptoms (2):
- Relief of symptoms;
- Improved tolerance to physical exercise;
- Improved health status.
2. Reducing future risks consists of (2):
- Preventing disease progression;
- Preventing and treating exacerbations;
- Decreased mortality.
Treatment
The main therapeutic measures are (2):
- Quit smoking
- Medicines - Bronchodilators (used according to the severity of the disease and the presence or absence of exacerbation)
- Respiratory rehabilitation
- Oxygen therapy
- Proper nutrition and lifestyle
Acronyms:
COPD - Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
WHO - World Health Organization
FEV1 - Forced expiratory volume in 1 second
FVC - Forced Vital Capacity
GOLD - Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease
mMRC – Modified Medical Research Council dyspnea scale
CAT – Scores de COPD assessment test
CCQ – Clinical COPD Questionnaire
SOBDA – Shortness of Breath with Daily Activities Questionnaire
Medinfar-2020-05-FL-02 drafted in April 2020
